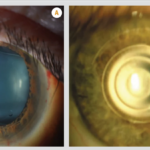
The field of ophthalmology has made remarkable advancements in recent years, with a primary objective of restoring vision to those who have lost it or are at risk of losing it. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness, have seen a significant transformation in surgical techniques. Innovations such as phacoemulsification, femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery, corneal astigmatism correction, and premium intraocular lenses have revolutionized cataract surgery, aiming to achieve optimal post-operative visual results. However, despite these advancements, pre and post-operative risks remain a concern.
The study I’m discussing today was conducted at the Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College, Surat, Gujarat, India. The study involved 200 cataract patients who underwent pre-operative examinations to assess the effectiveness of Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography scan (SD-OCT) in improving post-operative cataract surgery outcomes and preventing unforeseen complications.
During the Optical Coherence Tomography examination, abnormalities were detected in 65 out of 310 eyes (20.96%). The most common findings were epiretinal membranes in 22 eyes (7.09%) and pigment epithelial detachment in 14 eyes (4.5%). Other observed abnormalities included drusen (nine eyes), lamellar macular hole (five), vitreomacular traction (five), IS-OS junction abnormalities (four), retinal pigment epithelium alterations (two), juxtafoveal telangiectasia (one), foveal thinning (one), pseudovitelliform lesions (one), and spongy edema (one).
The various findings obtained provided valuable insights into the selection of intraocular lenses, informed the necessary surgical consents, and guided the therapeutic approach for each patient individually.
In conclusion, this comprehensive study underscores the essential role of Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography scan of the macula as a crucial step before cataract extraction. It helps prevent unexpected post-operative complications and potential legal issues. Such research should motivate ophthalmologists, especially cataract surgeons, to consider the pre-operative procedure as paramount. It is instrumental in identifying hidden macular pathologies, ensuring positive post-operative visual outcomes, and averting post-operative complications.